- Synonyms
- HR6B, Ubiquitin Carrier Protein B, Ubiquitin-protein Ligase B
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
- Molecular Weight
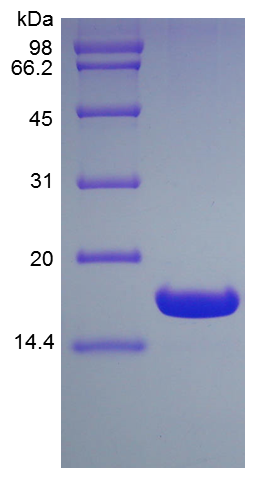
- Approximately 19.0 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 152 amino acids of human UBE2B and 14 a.a. vector sequence including 6 × His tag at N-terminus.
- AA Sequence
- MHHHHHHAMG QLRSMSTPAR RRLMRDFKRL QEDPPVGVSG APSENNIMQW NAVIFGPEGT PFEDGTFKLV IEFSEEYPNK PPTVRFLSKM FHPNVYADGS ICLDILQNRW SPTYDVSSIL TSIQSLLDEP NPNSPANSQA AQLYQENKRE YEKRVSAIVE QSWNDS
- Concentration
- See label.
- Purity
- > 95 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Data is not available.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Colorless liquid.
- Formulation
- A 0.2 µm filtered concentrated solution in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.6 with 125 mM NaCl, 10 % Glycerol, 5 % Trehalose, 1 mM DTT.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/µg of rHuUBE2B, His as determined by LAL method.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 6 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after opening.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
- Reference
- 1. Roest HP, van Klaveren J, de Wit J, et al. 1996. Cell, 86: 799-810.
2. Adegoke OA, Bedard N, Roest HP, et al. 2002. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 283: E482-9.
3. Kavakebi P, Hausott B, Tomasino A, et al. 2005. Mol Cell Neurosci, 29: 559-68.
4. Mulugeta Achame E, Wassenaar E, Hoogerbrugge JW, et al. 2010. BMC Genomics, 11: 367.
- Background
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 B belongs to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family and is encoded by the UBE2B gene in humans. The ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ubiquitin-carrier enzymes, take part in the second step in the ubiquitination reaction. In this reaction, E1 activates the ubiquitin by covalently attaching the molecule to its active site cysteine residue. The activated ubiquitin is then transferred to an E2 cysteine and then the E2 molecule binds E3 via a structurally conserved binding region. The ubiquitination reaction can modify proteins and regulate protein degradation. The UBE2B interacts with RAD18, UBR2 and WAC. Its protein sequence is 100 % identical to the mouse, rat, and rabbit homologs, which indicates that this enzyme is highly conserved in eukaryotic evolution.







 COA申请
COA申请
