- Synonyms
- Defensin beta1
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
- Molecular Weight
- Approximately 5.1 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 47 amino acids.
- AA Sequence
- GNFLTGLGHR SDHYNCVSSG GQCLYSACPI FTKIQGTCYR GKAKCCK
- Purity
- > 98 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The biological activity determined by a chemotaxis bioassay using CD34+ dendritic cells is in a concentration range of 100.0-1000.0 ng/ml.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered concentrated solution in 20 mM PB, pH 7.4, 130 mM NaCl.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/µg of rHuBD-1, 47a.a. as determined by LAL method.
- Reconstitution
- We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
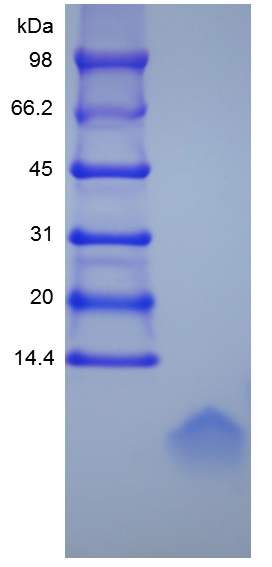
- Reference
- 1. Ryan LK, Dai J, Yin Z, et al. 2011. J Leukoc Biol, 90: 343-56.
2. Vatta S, Boniotto M, Bevilacqua E, et al. 2000. Hum Mutat, 15: 582-3.
3. Lee SH, Lim HH, Lee HM, et al. 2000. Acta Otolaryngol, 120: 58-61.
4. Wang YS, Wang GQ, Wen YJ, et al. 2007. Clin Cancer Res, 13: 6779-87.
- Background
- Defensins (alpha and beta) are cationic peptides with antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and enveloped viruses. They are 2-6 kDa proteins and take important roles in innate immune system. On the basis of their size and pattern of disulfide bonding, mammalian defensins are classified into alpha, beta and theta categories. β-Defensins contain a six-cysteine motif that forms three intra-molecular disulfide bonds. Four human β-defensins have been identified and they are expressed on some leukocytes and at epithelial surfaces. Because β-defensins is cationic peptides, they can therefore interact with the membrane of invading microbes, which are negative due to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) found in the cell membrane. Especially, they have higher affinity to the binding site compared to Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Furthermore, they can affect the stability of the membrane. The β-defensin proteins are expressed as the C-terminal portion of precursors and are released by proteolytic cleavage of a signal sequence and, in the case of BD-1 (36 a.a.), a propeptide region. Beta-defensin 1 may play a role in the pathogenesis of severe sepsis. Variation in human Beta Defensin-1 contributes to asthma diagnosis, with apparent gender-specific effects. Variation in human β-defensins 1 contributes to asthma diagnosis, with apparent gender-specific effects. Human BD1 is down-regulated in human prostatic and renal carcinomas.

 COA申请
COA申请
