- Synonyms
- Heregulin-beta1, HRG1
- Source
- Escherichia coli.
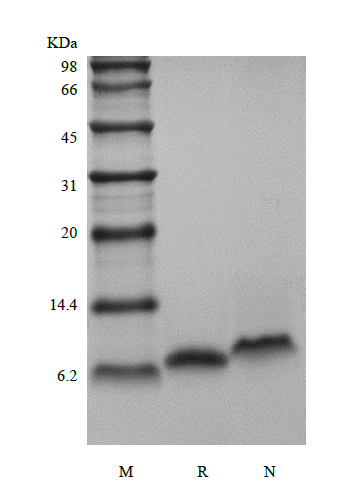
- Molecular Weight
- Approximately 7.0 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 61 amino acids.
- AA Sequence
- SHLVKCAEKE KTFCVNGGEC FMVKDLSNPS RYLCKCPNEF TGDRCQNYVM ASFYKAEELY Q
- Purity
- > 96 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Biological Activity
- Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The ED50 as determined by a cell proliferation assay using serum free human MCF-7 cells is less than 5 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of > 2.0 × 105 U/mg.
- Physical Appearance
- Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4.
- Endotoxin
- Less than 1 EU/μg of rHuNRG1-β2 as determined by LAL method.
- Reconstitution
- We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions.
- Stability & Storage
- Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- Usage
- This material is offered by Shanghai PrimeGene Bio-Tech for research, laboratory or further evaluation purposes. NOT FOR HUMAN USE.
- SDS-PAGE
- Reference
- 1. Shamir A, Kwon OB, Karavanova I, et al. 2012. J Neurosci, 32: 2988-97.
2. Malek RL, Toman RE, Edsall LC, et al. 2001. J Biol Chem, 276: 5692-9.
3. Zhang Z, Prentiss L, Heitzman D, et al. 2006. J Neurosci Res, 84: 1-12.
4. Law AJ, Shannon Weickert C, Hyde TM, et al. 2004. Neuroscience, 127: 125-36.
- Background
- Neuregulin 1 belongs to a family of structurally related polypeptide growth factors and is produced in numerous isoforms by alternative splicing, which allows it to perform a wide variety of functions. These isoforms include heregulins (HRGs), glial growth factors (GGFs) and sensory and motor neuron-derived factor (SMDF). They all have the Ig and EGF-like domain, and can bind to ErbB3 and ErbB4 receptor tyrosin kinases. This binding induces ErbB3 and ErbB4 heterodimerization with ErbB2, stimulating intrinsic kinase activity, which leads to tyrosine phosphorylation. NRG1 isoforms have functions of inducing the growth and differentiation of epithelial, neuronal, glial, and other types of cells.







 COA申请
COA申请
